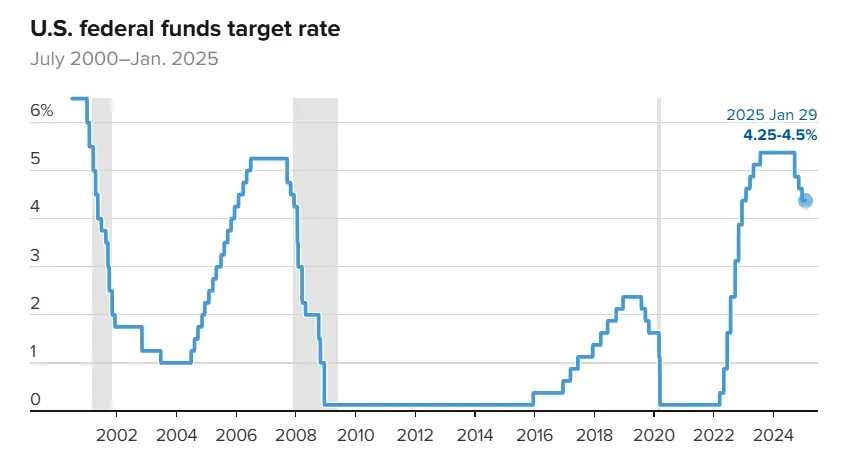
In light of the current economic and political conditions, the Federal Reserve has decided to keep its key interest rate unchanged, adopting a cautious approach in facing challenges related to inflation and economic growth. The Fed has maintained the interest rate within the range of 4.25% – 4.5%, after cutting it three times since September 2024.
This decision comes at a time when inflation remains high, recording 2.4% in November, exceeding the Fed’s target of 2%. Despite continued economic growth, with GDP increasing by 2.3% in Q4 2024, the Federal Reserve remains cautious about taking further steps to cut interest rates.
In this context, Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell emphasized that any adjustments to monetary policy will only be made if there is significant progress in reducing inflation or if there is weakness in the labor market. Projections indicate that the Fed will not make any further rate cuts until at least June 2025.
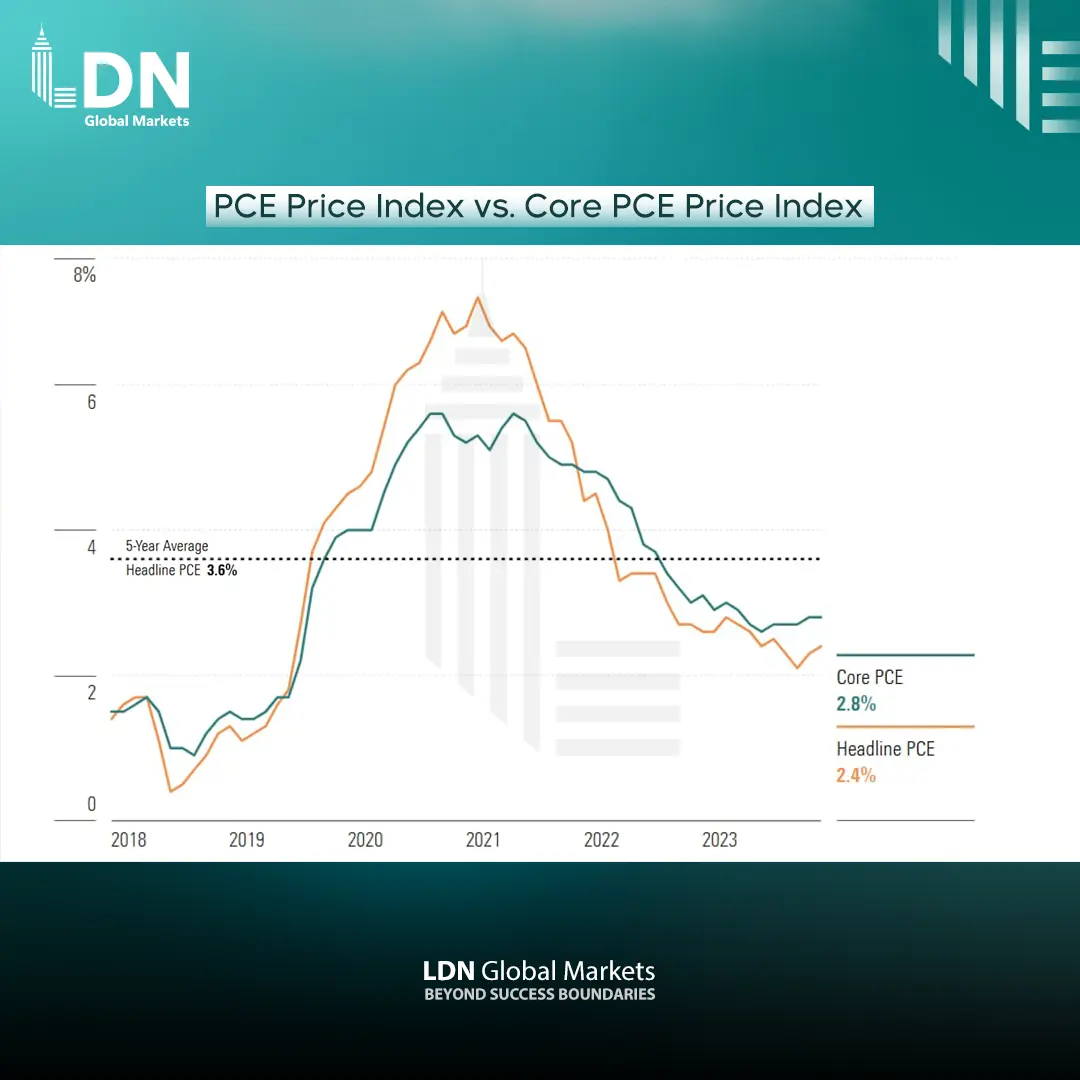
The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) report for January is expected to show continued core inflation growth, with the overall index rising by 0.4% month-over-month and 2.4% year-over-year. The core PCE index, which excludes food and energy, is also expected to rise by 0.3% monthly and 2.8% annually. Despite rising fuel prices, economists believe there is ongoing progress in reducing inflation, with expectations that the core inflation rate could decline to around 2.2% by March, provided there are no additional inflationary spikes.
Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve is expected to keep interest rates steady in the near future. On the other hand, as part of efforts to support the European economy, the European Central Bank (ECB) has announced a reduction in its key interest rate in a move aimed at stimulating economic growth and enhancing stability in the Eurozone.
The ECB has lowered its key interest rate from 3.15% to 2.9% in an effort to boost economic growth in the Eurozone. This decision aims to make borrowing more affordable, encouraging increased investments, boosting consumer spending, and stimulating business activity.
This adjustment in monetary policy reflects the ECB’s strategy to support economic recovery while maintaining control over inflation. This decision is expected to have a significant impact on loans, mortgages, and financing conditions in the coming months, potentially contributing to overall economic stimulation in the region.





