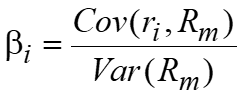Cannot fetch data from server.
Questions and Answers
1- What is Speculator?
A speculator is an investor who takes on more risk while trading derivatives, commodities, bonds, stocks, or currencies in the hopes of making more money than usual. In an attempt to make rapid, significant profits, speculators incur significant risks, particularly when it comes to projecting future market changes.
2- What is Broker?
Brokers are individuals, either legally or privately, who act as intermediaries or negotiators on behalf of buyers and sellers of stocks or money in trading meetings. A broker may offer additional services while working under his client’s name, on their behalf, and at their expense. When brokers complete orders for customers, they are paid a commission bonus.
3- What is Inflation?
The general level of prices for products and services has been steadily rising. The rise is expressed as a percentage per year. A smaller portion of an item or service can be purchased with each dollar you own as inflation increases.
4- What is Deflation?
The purchasing power of money and wages are higher during deflation than they would have been otherwise. While the phrases are sometimes confused and used interchangeably, this is different from price deflation, which is a general decline in the level of prices.
5- What is Liquidity?
The ability of a security or asset to be swiftly purchased or sold on the market without depressing the asset’s price is known as liquidity.
6- What is Cashflow?
It’s the movement of cash in and out of a business from day-to-day direct trading and other non-trading or indirect effects, such as capital expenditure, tax and dividend payments.
7- What is Net Present Value (NPV)?
the Net Present Value (NPV) holds great importance when making investment decisions in business. NPV serves as a comprehensive assessment of the future cashflow (revenues minus costs, also known as net benefits) that will be obtained from a specific investment, subtracting the initial investment cost. Logically, if a proposal exhibits a positive NPV, it signifies profitability and deserves careful consideration. Conversely, if the NPV is negative, the proposal is deemed unprofitable and should not be pursued.
8- What is Forex Market?
Foreign exchange, commonly known as ‘Forex’ or ‘FX’, is the exchange of one currency for another at an agreed exchange price on the over the counter (OTC) market. Forex is the world’s most traded market, with an average turnover in excess of US $5.3 trillion per day.
9- What is the most Commonly Traded Currency Pair?
EUR/USD (Euro to the US Dollar), USD/JPY (US Dollar to the Japanese Yen), GBP/USD (British Pound to the US Dollar), AUD/USD (US Dollar to the Australian Dollar), USD/CHF (US Dollar to the Swiss Franc), USD/CAD (US Dollar to the Canadian Dollar), EUR/JPY (Euro to the Japanese Yen), EUR/GBP (Euro to the British Pound)
10- What is Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA)?
An investment technique of buying a fixed dollar amount of a particular investment on a regular schedule, regardless of the share price. The investor purchases more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high. The premise is that DCA lowers the average share cost over time, increasing the opportunity to profit. The DCA technique does not guarantee that an investor won’t lose money on investments. Rather, it is meant to allow investment over time instead of investment as a lump sum.
11- What is capital asset pricing model (CAPM)?
The capital asset pricing model (CAPM) describes the relationship between risk and expected return, and it serves as a model for the pricing of risky securities. … Required (or expected) Return = RF Rate + (Market Return – RF Rate)*Beta.
12- What is Asset Allocation?
Asset allocation is the implementation of an investment strategy that attempts to balance risk versus reward by adjusting the percentage of each asset in an investment portfolio according to the investor’s risk tolerance, goals and an investment time frame.
13- What are Lots in Forex?
Historically, currencies were traded in specific amounts called lots. The standard size for a lot is 100,000 units. There are also mini-lots of 10,000 and micro-lots of 1,000.
To take advantage of relatively small moves in the exchange rates of currency, we need to trade large amounts in order to see any significant profit (or loss).
14- What is Currency Pair?
A currency pair is the quotation and pricing structure of the currencies traded in the forex market; the value of a currency is a rate and is determined by its comparison to another currency. The first listed currency of a currency pair is called the base currency, and the second currency is called the quote currency.
For example, the currency pair EUR/USD means the base currency is the Euro while the quote currency is the US Dollar.
15- What are PIPS in Forex?
Pip = “price interest point“
A pip measures the amount of change in the exchange rate for a currency pair.
For currency pairs displayed to four decimal places, one pip is equal to 0.0001. Yen-based currency pairs are an exception and are displayed to only two decimal places (0.01).
Some brokers now offer fractional pips to provide an extra digit of precision when quoting exchange rates for certain currency pairs. A fractional pip is equivalent to 1/10 of a pip.
16- What is Arbitrage in Forex?
In Forex, arbitrage allows retail forex traders to make a profit with no open currency exposure. The strategy involves acting fast on opportunities presented by pricing inefficiencies, while they exist.
This type of arbitrage trading involves the buying and selling of different currency pairs to exploit any inefficiency of pricing.
17- What is RSI?
The RSI measures the ratio of up-moves to down-moves and normalizes the calculation so that the index is expressed in a range of 0-100. If the RSI is 70 or greater, then the instrument is assumed to be overbought (a situation in which prices have risen more than market expectations). An RSI of 30 or less is taken as a signal that the instrument may be oversold (a situation in which prices have fallen more than the market expectations).
18- What is Stochastic Oscillator?
This is used to indicate overbought/oversold conditions on a scale of 0-100%. The indicator is based on the observation that in a strong up trend, period closing prices tend to concentrate in the higher part of the period’s range. Conversely, as prices fall in a strong down trend, closing prices tend to be near to the extreme low of the period range. Stochastic calculations produce two lines, %K and %D that are used to indicate overbought/oversold areas of a chart.
Divergence between the stochastic lines and the price action of the underlying instrument gives a powerful trading signal.
19- What is the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)?
The (WACC) is a calculation of a firm’s cost of capital in which each category of capital is proportionately weighted. All sources of capital, including common stock, preferred stock, bonds and any other long-term debt, are included in a WACC calculation.
A firm’s WACC increases as the beta and rate of return on equity increase, as an increase in WACC denotes a decrease in valuation and an increase in risk.
20- What is the concept of trends in Forex?
A trend refers to the direction of prices. Rising peaks and troughs constitute an up trend; falling peaks and troughs constitute a downtrend that determines the steepness of the current trend. The breaking of a trend line usually signals a trend reversal. Horizontal peaks and troughs characterize a trading range.
Moving averages are used to smooth price information in order to confirm trends and support and resistance levels. They are also useful in deciding on a trading strategy, particularly in futures trading or a market with a strong up or down trend.
21- What is the International Monetary Fund (IMF)?
The IMF is an international organization headquartered in Washington DC, of 189 countries that work together to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world.
22- What is the Federal Trade Commission (FTC)?
The FTC is an independent agency of the United States Government and it’s principal mission is the promotion of consumer protection and the elimination and prevention of anticompetitive business practices, such as coercive monopoly.
23- What is Fibonacci retracement?
Fibonacci retracement lines are based on the Fibonacci Sequence and are considered a “predictive” technical indicator providing feedback on possible future exchange rate levels. There are some traders who swear by the accuracy by which Fibonacci Retracements can predict future rates, while others argue that Fibonacci numbers are more art, than science.
Given their popularity and widespread usage by technical analysts, you should at least know how to interpret Fibonacci numbers.
24- What is the Credit Rating Agency (CRA)?
A CRA, also called a ratings service, is a company that assigns credit ratings, which rate a debtor’s ability to pay back debt by making timely interest payments and the likelihood of default. An agency may rate the creditworthiness of issuers of debt obligations, of debt instruments, and in some cases, of the servicers of the underlying debt, but not of individual consumers.
Credit rating is a highly concentrated industry, with the “Big Three” credit rating agencies controlling approximately 95% of the ratings business. Moody’s Investors Service and Standard & Poor’s (S&P) together control 80% of the global market, and Fitch Ratings controls a further 15%.
25- What is Fibonacci retracement?
Fibonacci retracement lines are based on the Fibonacci Sequence and are considered a “predictive” technical indicator providing feedback on possible future exchange rate levels. There are some traders who swear by the accuracy by which Fibonacci Retracements can predict future rates, while others argue that Fibonacci numbers are more art, than science.
Given their popularity and widespread usage by technical analysts, you should at least know how to interpret Fibonacci numbers.
26- What is the Securities & Exchange Commission?
The SEC is an agency of the United States Government, and it holds primary responsibility for enforcing the federal securities laws, proposing securities rules, and regulating the securities industry, the nation’s stock and options exchanges, and other activities and organizations, including the electronic securities markets in the United States.
27- What is the Discount Rate?
The Federal Reserve System directly sets the “discount rate”, which is the interest rate for “discount window lending”, overnight loans that member banks borrow directly from the Fed. This rate is generally set at a rate close to 100 basis points above the target federal funds rate. The idea is to encourage banks to seek alternative funding before using the “discount rate” option.
The equivalent operation by the European Central Bank is referred to as the “Marginal Lending Facility.”
28- What is the Reserve requirements?
An instrument of monetary policy adjustment employed by the Federal Reserve System is the fractional reserve requirement, also known as the required reserve ratio.
The required reserve ratio sets the balance that the Federal Reserve System requires a depository institution to hold in the Federal Reserve Banks, which depository institutions trade in the federal funds market.
29- What is the Federal Reserve System (FED)?
Also known as the Federal Reserve or simply the Fed, is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act in response to a series of financial panics that showed the need for central control of the monetary system if crises are to be avoided.
30- What is Monetary Policy?
This is the process by which the monetary authority of a country, like the central bank or currency board, controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.
31- What is Bull Market?
This refers to a condition in which securities prices fall and widespread pessimism causes the stock market’s downward spiral to be self-sustaining. Investors anticipate losses as pessimism and selling increases. Although figures vary, a downturn of 20% or more from a peak in multiple broad market indexes, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) or Standard & Poor’s 500 Index (S&P 500), over a two-month period is considered an entry into a bear market.
32- What is Bull Market?
This refers to a financial market of a group of securities in which prices are rising or are expected to rise. The term “bull market” is most often used to refer to the stock market but can be applied to anything that is traded, such as bonds, currencies (forex market) and commodities.
33- What is the Commercial Banks Role in Forex Market?
These are financial intermediaries that accept deposits from legal and private persons, take advantage of investing this money, return it to depositors, close and operate bank accounts. Every country has some big commercial banks that are able to influence currency rates.
34- What is Credit Default Swap (CDS)?
This particular type of swap is designed to transfer the credit exposure of fixed income products between two or more parties. In a credit default swap, the buyer of the swap makes payments to the swap’s seller up until the maturity date of a contract. In return, the seller agrees that, in the event that the debt issuer defaults or experiences another credit event, the seller will pay the buyer the security’s premium as well as all interests payments that would have been paid between that time and the security’s maturity.
35- What is Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDO)?
A CDO is a type of structured asset-backed security (ABS). Originally developed for the corporate debt markets, over time CDOs evolved to encompass the mortgage and mortgage-backed security (“MBS”) markets.
36- Why we use Candlestick chart?
The purpose of candlestick charting is strictly to serve as a visual aid, since the exact same information appears on other charts.
-
Candlesticks are easy to interpret and are a good place for a beginner to start figuring out chart analysis.
-
Candlesticks are easy to use. Your eyes adapt almost immediately to the information in the bar notation.
-
Candlesticks and candlestick patterns have cool names such as the shooting star, which helps you to remember what the pattern means.
•Candlesticks are good at identifying marketing turning points – reversals from an uptrend to a downtrend or a downtrend to an uptrend.
37- When NOT to Trade Forex?
-
Bank Holidays
-
Friday Afternoons and Weekends
-
End of December
-
When Angry or Frustrated
-
Asian Sessions
-
Release of News Events
-
Market Closing Time
-
Overnight
38- What are the Currency nicknames?
-
Single Currency – EUR (Euro)
-
Loonie – CAD (Canadian dollar)
-
Swissie – CHF (Swiss franc)
-
Aussie – AUD (Australian dollar)
-
Kiwi – NZD (New Zealand dollar)
-
Greenback, Buck – USD (U.S. dollar)
-
Sterling, Pound sterling – GBP (British pound)
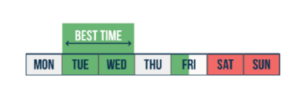
39- The Best Time of the Week to Trade Forex?
Research has found that the biggest movements in four of the major currency pairs – namely EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD\JPY and USD/CHF – are observed on Tuesdays and Wednesdays. These days generally show the biggest movements in currencies as major data releases related to the economy are usually released on these days.
Fridays are busy as well, but only until 12am. During the second half of Friday, movements can often be unpredictable since major banks, hedge funds and financial institutions will close some of their positions for safety reasons over the weekend.
40- How do you calculate pip value?
The value of a pip changes based on the currency, the amount traded and the exchange rate. For U.S. Dollar accounts, the pip value of currency pairs not based in U.S. Dollars is consistent with the amount that is being traded. On one standard lot, the pip value is $10. The value of a mini lot ($1) and micro lot ($0.10) is consistent with how much is being traded.
When the U.S. Dollar is the base currency, the pip value varies based on the exchange rate.
To calculate the pip value of those currency pairs, follow this formula:
Pip Value = (Pip in decimal places * Trade Size) / Exchange Rate
For example, for 1 standard lot of USD/CAD at the price of 1.30, the pip value is:
Pip Value = (0.0001 * 100,000) / 1.30 = $7.69
If you were in the same 1 standard lot of USD/CAD trade at 1.20, the pip value would be higher:
Pip Value = (0.0001 * 100,000) / 1.20 = $8.33
The pip value does not change based on whether you are long or short the currency.
41- What is ADR (American Depositary Receipt)?
A security representing shares in a foreign company traded on U.S. exchanges.
42- What is Alpha Generation?
The process of achieving excess returns above a benchmark index.
43- What is Alpha?
A measure of an investment’s performance compared to a benchmark index, indicating the ability of a portfolio manager to generate excess returns.
44- What is Bear Market?
A market characterized by falling prices and pessimism among investors.
45- What is Beta Coefficient?
A market characterized by falling prices and pessimism among investors.
46- What is Beta?
A measure of a stock’s volatility in relation to the overall market.
47- What are Blue Chip Stocks?
Shares of well-established, financially stable, and typically large-cap companies known for their reliability.
48- What is Book Value?
The net asset value of a company calculated by subtracting its liabilities from its assets.
49- What is Buy-Side Analyst?
An analyst who works for an institution that buys and holds securities, such as mutual funds or hedge funds.
50- What is CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate)?
The mean annual growth rate over a specified time period, useful for assessing investment returns.
51- What is Capital Allocation?
The process of deciding how to invest a company’s resources to achieve its objectives.
52- What is Catalyst?
An event or factor that can significantly affect a stock’s price or performance.
53- What is Convertible Bond?
A bond that can be converted into a specified number of company shares.
54- What are Dark Pools?
Private electronic trading platforms used by institutional investors for large trades.
55- What is Earnings Call?
A conference call where a company’s management discusses its financial results and outlook with analysts and investors.
56- What is IPO (Initial Public Offering)?
The first sale of a company’s stock to the public.
57- What is Market Capitalization Weighting?
A stock index weighting method based on the total market value of a company’s outstanding shares.
58- What is Market Risk Premium?
The extra return an investor expects for taking on the risk of investing in equities instead of risk-free assets.
59- What is Proxy Statement?
A document that provides information about a company’s management and board of directors.
60- What is R-Squared?
A statistical measure that represents the proportion of a security’s movements that can be explained by movements in a benchmark index.
61- What is Sector Rotation?
A strategy involving shifting investments between different sectors based on economic conditions and market trends.
62- What is Sell-Side Analyst?
An analyst who works for a brokerage or financial institution that sells securities to investors.
63- What is Systematic Risk?
Risk associated with the overall market or economy, also known as market risk.
64- What is Unsystematic Risk?
Risk specific to a particular company or industry, not related to overall market conditions.
65- What is Treasury Stock?
Shares of a company’s own stock that it has repurchased and holds in its own treasury.
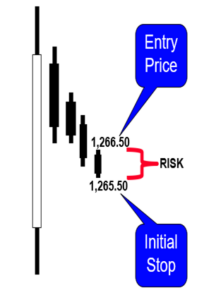
66- How many contacts/lots should I Buy or Sell?
– Risk = Entry – Initial Stop:
1266.50 – 1265.50 = 50.00/contract.![]()
– Position Sizing is Crucial:
Risk should not exceed 1% to 2% of your equity on any trade.
– Account Equity = $20,000:
Max Risk = $20,000 x 1% = $200.
Max contracts = Max Risk Amount / Risk per Contract.
Max contracts = $200.00/$50.00 = 4 contracts.
67- What is Budgetary Deficit?
A budgetary deficit occurs when governmental expenditure exceeds its income. Expenditure stimulates the economy by creating jobs and stimulating demand. However, this can also lead to deficit financing and inflation. Both these, if not checked, can result in spiralling prices. To control and cut deficits governments normally cut governmental.
expenditure This would also result in a fall in money supply and a consequent fall in demand which will check inflation.
All developing economies suffer from budget deficits as governments spend to improve the infrastructure — build roads, power stations and the like.
68- What is Domestic Savings and Its Utilization?
Domestic savings refers to the total amount of money that residents of a country save rather than spend. This includes both personal savings and business/corporate savings. The utilization of domestic savings is an important aspect of economic development and growth.
Some key points about the utilization of domestic savings:
1- Investment: Domestic savings are typically channelled into investment, such as building infrastructure, expanding businesses, and financing new projects. This increases the productive capacity of the economy.
2- Reducing Reliance on External Borrowing: When a country has high levels of domestic savings, it can rely less on foreign borrowing to finance investment and development, making it less vulnerable to external economic shocks.
3- Fuelling Economic Growth: Productive investment of domestic savings can stimulate economic growth by increasing employment, productivity, and incomes.
4- Funding the Public Sector: Governments can use domestic savings, through bond issuances and other mechanisms, to fund public expenditure on things like healthcare, education, and social welfare programs.
5- Promoting Financial Stability: A strong domestic savings base can make the financial system more resilient and less prone to external shocks and capital flight.
The efficient utilization of domestic savings is an important policy goal for many developing and emerging economies, as it can reduce their dependence on foreign capital and support sustainable economic development. Governments often implement policies to encourage household and corporate saving, and to channel those savings into productive investments.
69- What is Government Policy?
Government policy refers to the course of action or set of principles adopted and pursued by a government to address various issues and achieve desired outcomes for the country and its citizens. Government policies are typically formulated and implemented through legislation, regulations, and administrative actions.
Some key aspects of government policy include:
1- Economic Policy: This covers areas such as fiscal policy (taxation, spending, and borrowing), monetary policy (interest rates, money supply), trade policy, and policies to promote economic growth, employment, and development.
2- Social Policy: Policies related to social welfare, healthcare, education, housing, and income distribution, with the goal of improving the well-being and quality of life for citizens.
3- Foreign Policy: The government’s approach to international relations, including diplomacy, national security, and policies on issues like immigration, trade, and global cooperation.
4- Environmental Policy: Policies to address environmental challenges, such as pollution control, natural resource management, and climate change mitigation and adaptation.
5- Regulatory Policy: The rules, regulations, and guidelines set by the government to govern the behaviour of businesses, industries, and individuals in the public interest.
Governments use a variety of policy instruments to implement their agenda, such as legislation, taxation, subsidies, public spending, and administrative controls. The development and execution of government policy involves input from various stakeholders, including policymakers, experts, interest groups, and the general public.
70- What is Taxation?
The level of taxation in a country has a direct effect on the economy. If tax rates are low, people have more disposable income. In addition, they have an incentive to work harder and earn more. And an incentive to invest. This is good for the economy. It is interesting to note that in every economy there is a level between 35% to 55% where tax collection will be the highest. While the tax rates may go up, collection will decline.
71- What is the Threat of Nationalization?
The threat of nationalization is a real threat in many countries — the fear that a company may become nationalized. With very few exceptions, nationalized companies are historically less efficient than their private.
sector counterparts. If one is dependent on a company for certain supplies, nationalization could result in supplies becoming erratic. In addition, the fear of nationalization chokes private investment and there could be a flight of capital to other countries.
72- What is Foreign Debt and the Balance of Trade?
Foreign debt and the balance of trade are two important economic concepts related to a country’s international financial position.
Foreign Debt:
1- Foreign debt refers to the total amount of money a country owes to foreign lenders, such as other governments, international organizations, or private investors.
2- Countries borrow from foreign sources to finance budget deficits, fund development projects, or supplement domestic savings for investment.
3- High levels of foreign debt can make a country vulnerable to exchange rate fluctuations and changes in global interest rates and can constrain a country’s ability to implement independent economic policies.
4- Governments often seek to manage and reduce foreign debt through policies like fiscal consolidation, debt restructuring, or negotiating more favourable loan terms.
73- What is Balance of Trade?
Balance of Trade:
1- The balance of trade is the difference between a country’s exports and imports of goods and services.
2- A trade surplus occurs when exports exceed imports, while a trade deficit happens when imports are greater than exports.
3- The balance of trade is a key component of a country’s current account balance, which also includes income from foreign investments and net transfer payments.
4- Running persistent trade deficits can lead to the accumulation of foreign debt, as a country needs to borrow to finance the excess of imports over exports.
5- Governments may implement trade policies, such as tariffs, quotas, or exchange rate management, to try to improve the balance of trade.
The interplay between foreign debt levels and the balance of trade is an important consideration in a country’s overall economic and financial strategy. Policymakers often need to balance the benefits and risks associated with foreign borrowing and trade flows.
74- What are Restrictive Practices?
Restrictive practices refer to actions or policies implemented by businesses, industries, or governments that limit or restrict competition, market access, or economic freedom.
Some examples of restrictive practices include:
1- Monopolistic Practices:
– Abuse of a dominant market position to exclude competitors.
– Price fixing or collusion among major players in an industry.
2- Anticompetitive Agreements:
– Cartels and other arrangements to limit competition.
– Exclusive dealing contracts that foreclose market access.
3- Trade Barriers:
– Tariffs, quotas, or other import restrictions.
– Non-tariff barriers like complex regulations or licensing requirements.
4- State-Owned Enterprises:
– Preferential treatment or subsidies for state-owned firms
– Restrictions on private sector participation in certain industries
5- Intellectual Property Abuse:
– Excessive use of patents, trademarks or copyrights to limit competition.
– Refusal to license essential technologies.
Restrictive practices can have negative economic consequences, such as:
a- Higher prices and reduced consumer choice
b- Stifling of innovation and technological progress
c- Inefficient allocation of resources
d- Barriers to international trade and investment
Governments often enact competition laws and policies to prevent or address restrictive practices and promote a more open and competitive market environment. International trade agreements also aim to reduce restrictive practices that distort global commerce.
Striking the right balance between necessary regulation and encouraging healthy competition is an ongoing challenge for policymakers when addressing restrictive practices.
75- What is the usage of artificial intelligence and machine learning in financial analysis?
AI and machine learning can automate routine tasks, identify patterns in data, and provide predictive insights, enhancing financial analysis. Human judgment remains crucial for interpreting results and making informed decisions.
76- What are the different valuation methods for a company?
Valuation methods include Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), Comparable Company Analysis (CCA), and Precedent Transaction Analysis (PTA). DCF, considering a company’s future cash flows discounted to present value, is preferred.
77- How do you assess the risk of a portfolio of investments?
Using beta, standard deviation, and value at risk (VaR), alongside diversification and correlations among assets, ensures alignment with investor risk tolerance and objectives.
78- How to forecast the company's revenue?
Using historical data, market research, and industry trends, I analyse factors affecting sales and validate forecasts through sales and marketing team discussions.
79- What is the WACC (Weighted Average Cost of Capital)?
WACC is the weighted average cost of debt and equity, representing the minimum return a company must earn to satisfy investors. It’s used as the discount rate in DCF analysis.
80- What is a sensitivity analysis and why is it important in financial modelling?
Sensitivity analysis changes a single variable in a model to observe its impact on outcomes. It identifies significant variables and assesses the model’s robustness.
81- What is the efficient market hypothesis?
This hypothesis suggests all information is already reflected in security prices, making superior returns through analysis impossible. However, market inefficiencies can be exploited with thorough research.
82- How do you incorporate macroeconomic factors into your financial analysis?
Monitoring GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates helps assess their impact on a company’s performance, especially revenue and cost projections.
83- What are the risk factors we consider when evaluating an investment opportunity?
Risks considered include market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, regulatory risk, and operational risk, enabling informed investment decisions and risk mitigation strategies.
84- What is the difference between correlation and causation in financial analysis?
Correlation indicates a statistical relationship between two variables, while causation suggests one directly influences the other. Analysts should use additional evidence to establish causation.
85- How do we evaluate the competitive positioning of a company within its industry?
Assessing market share, growth prospects, product differentiation, and adaptability to industry trends, alongside analysing competitive advantages and barriers to entry, evaluates competitive positioning.
86- How to explain the Black-Scholes model and its significance in options pricing?
The Black-Scholes model calculates the theoretical price of European-style options, providing a framework for understanding financial derivatives pricing.
87- What is the qualitative information when conducting financial analysis?
Qualitative factors like management quality and industry reputation are incorporated through interviews, industry reports, and consideration of non-financial factors affecting performance.
88- What are the Economic Moats?
Economic moats, representing a company’s competitive advantages protecting its market position, are assessed for factors like brand recognition, cost leadership, and network effects influencing investment decisions.
89- How do we use regression analysis in financial forecasting and modelling?
Regression analysis identifies relationships between variables, predicting impacts of changes in independent variables (e.g., interest rates) on dependent variables (e.g., sales).
90- What is the successful financial analyst needs to excel his role?
A successful financial analyst needs strong analytical skills, attention to detail, proficiency with large datasets, deep understanding of financial markets, excellent communication skills, adaptability, and a commitment to ethics and integrity.
91- How do you determine the appropriate dividend policy for a company?
Considering the company’s financial goals, cash flow, capital requirements, and investor expectations helps formulate a suitable dividend policy.
92- What is the approach to scenario analysis in financial modelling?
Creating multiple scenarios with different assumptions assesses potential outcomes, considering base case, best-case, and worst-case scenarios to understand financial impacts under varying conditions.
93- What are the risks associated with investing in emerging markets?
Risks include political instability, currency fluctuations, and regulatory oversight. In-depth country risk analysis and potential mitigations are assessed.
94- What is the impact of changes in interest rates on fixed-income securities?
Interest rate changes affect fixed-income security values inversely; rising rates decrease bond values, and vice versa, due to their relationship with bond prices.
95- Why are stock returns so high?
Investors need to pay a risk premium for equities compared to relatively risk-free assets like government securities.
The risk-free rate plus a risk premium equals the projected return on a hazardous security.
Risk-free rate plus risk premium equals expected return.
Expected return –risk-free rate equals risk premium.
96- How to Measure Risk?
To quantify risk, we can utilize the expected rate of return’s variance or standard deviation.
The weighted average of each observation’s squared deviation from the mean is measured by variance, also known as standard deviation.
97- Types of risks?
Market Risk: Risks pertaining to the entire economy that impact the stock market. Likewise known as “systematic risk.”
Unsystematic Risk: Hazards that are specific to that company. Like “firm-level risk.”
98- Can we reduce risk?
Yes, diversification helps lower risk. To do this, we can allocate our funds across a variety of assets or create a portfolio of various assets.
99- How to measure Market Risk?
Market-Based Portfolio
It is an assortment of all the economic assets. In actuality, the market portfolio is represented by a wide stock market index, such the S&P 500. The symbol for the market return is Rm
Beta (β).
The relationship between a stock’s return and the market portfolio’s return
Mathematically,