Capital market efficiency (CME) :
-
CME means that the market rationally prices securities so that the current price of each security at any given moment represents the best estimate of its ‘true’ value.
-
CME would imply that all available information bearing on the value of a particular security is rapidly and rationally taken into account in its price.
-
It is reasonable to believe that CME could exist in practice because many skilled individuals with the financial weight to affect security prices constantly assess the value of those securities and monitor their market prices.
-
The current price of any security represents a consensus view of the security’s current worth – its price is the result of the actions of buyers and sellers, each with different perceptions of the value of the security.
The evidence on CME :
-
Research studies have been conducted that look at efficiency at three different levels:
-
weak form (WF).
-
semi-strong form (SSF).
-
strong form (SF).
-
-
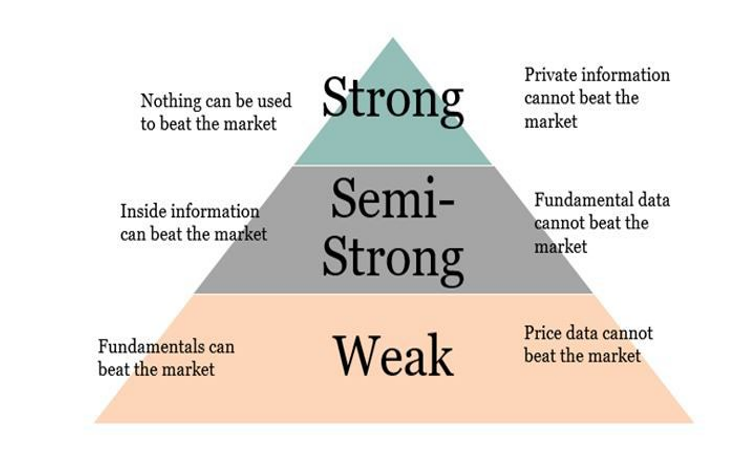
WF efficiency would exist if it were not possible to make abnormal profits from security investing relying on past security price movements (for example, with the use of charts) or technical rules to indicate when to buy and sell.
-
Evidence shows that the world’s leading markets are WF efficient.
-
SSF efficiency would exist if it were not possible to make abnormal profits from security investing relying on the analysis of publicly available information to indicate when to buy and sell.
-
Evidence shows that the world’s leading stock markets are SSF efficient.
-
SF efficiency would exist if it were not possible to make abnormal profits from security investing relying on the analysis of information available only to insiders to indicate when to buy and sell.
-
Evidence shows that the world’s leading markets are not SF efficient.
Implications of CME :
-
Implication for investors: only if they have access to information not available to the public can they expect, except by chance, to make better-than-average returns, given the risk class of the securities concerned.
-
Implications for financial managers:
-
It is difficult to fool investors.
-
The market rationally values the business.
-
Efforts to enhance share value should have that effect.
-
Managers may have a short-term interest in withholding information.
-
The LSE rationally values assets with risky returns.





