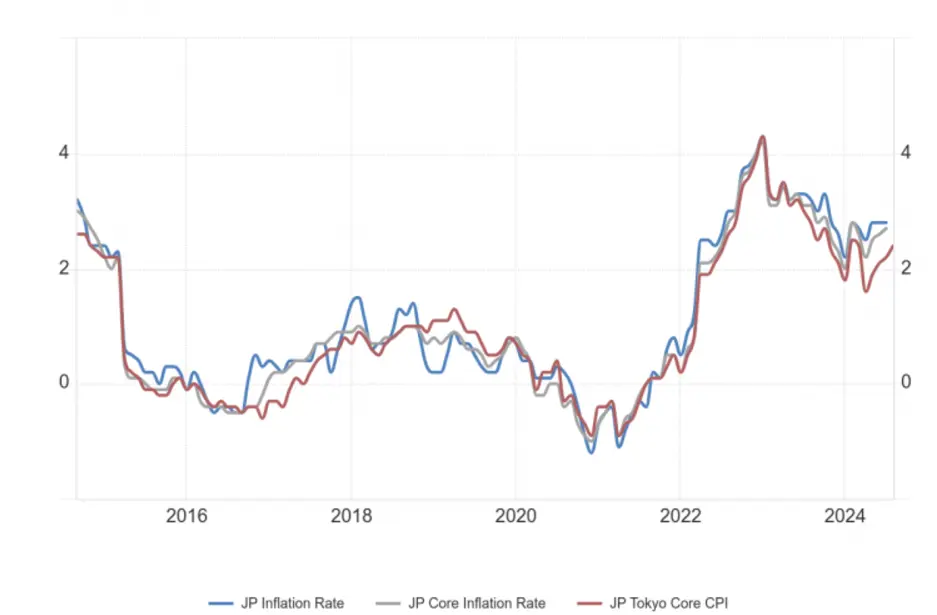
Japan has kept interest rates low for a long time to combat deflation, boost economic growth, and address challenges like its aging population and low inflation. The Bank of Japan (BOJ) has used strategies such as keeping rates low and unconventional methods like quantitative easing to encourage spending, investment, and inflation, while also managing high public debt. While results have been mixed, these efforts have helped stabilize the economy, support exports, and foster recovery during a long period of slow growth. The key question now is: what actions has the BOJ taken recently?